“A Brighter Future for Eczema: Vitamin D and its Healing Properties”
Eczema, also known as Atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin and can be triggered by a variety of factors, including genetics, environmental factors, and a compromised immune system.

Although our skin requires various vitamins and minerals to function adequately, vitamin D is particularly important. It regulates cell growth, reduces inflammation, and promotes wound healing. It also supports immune function, maintains healthy bones, and reduces the risk of certain diseases, making it essential for overall health and glowing skin.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin naturally synthesized in the skin through exposure to sunlight; it plays a crucial role in modulating the immune system and reducing inflammation, which could help alleviate Eczema symptoms.
Vitamin D, also known as cholecalciferol, is an active steroid hormone essential for all-around health and well-being, including the health of our skin.
Vitamin D is crucial in maintaining healthy bones and teeth, supporting the immune system, and promoting healthy skin.
When it comes to the skin, vitamin D helps to regulate the growth and differentiation of skin cells, and it has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to calm and soothe inflamed or irritated skin. Vitamin D also helps to boost the production of antimicrobial peptides, which are proteins that help to fight off harmful bacteria and viruses.
How is Vitamin D produced in our body?
Vitamin D synthesis happens from two sources: Sunlight and Food.
When we get sunlight, our skin produces a form of vitamin D called vitamin D3. If we eat certain foods or take supplements, we can also get vitamin D2 or D3.

Then in our body, vitamin D3 is transformed into a new form called 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) in the liver. This new form is carried in our blood to the kidneys, changing it into an even more unique form called 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D (1,25(OH)D). This new form can activate the vitamin D receptor (VDR) and affect the expression of certain genes that control various bodily functions like calcium metabolism, immunity, cell growth, and more.
One of the most important roles of vitamin D in the body is its regulation of calcium metabolism.
Why is vitamin D essential in regulating our immune system?
Vitamin D is essential in regulating the immune system and reducing skin inflammation. The immune mechanism by which vitamin D reduces skin inflammation involves several steps.
Vitamin D receptors are found on various immune cells, including T, B, and antigen-presenting cells. Vitamin D plays a vital role in immune function, modulating innate and adaptive immune responses.
In the context of Eczema and skin inflammation, vitamin D plays a role in several immune mechanisms that help reduce inflammation. One of these mechanisms involves the production of cathelicidin, an antimicrobial peptide that helps fight off infections. Cathelicidin also has anti-inflammatory properties, and it can help reduce skin inflammation. Vitamin D stimulates the production of cathelicidin by immune cells, including keratinocytes, which are cells that make up the outer layer of the skin.
In addition to promoting the production of cathelicidin, vitamin D can also inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are the signaling molecules that promote inflammation in the body.
By reducing the production of these cytokines, vitamin D can help dampen the inflammatory response in the skin.
Furthermore, vitamin D can promote the differentiation and activity of regulatory T cells, which are a type of immune cell that helps to control the immune response and prevent excessive inflammation.
Regulatory T cells act as “brakes” on the immune system, and they help to prevent autoimmune reactions and excessive inflammation. By promoting the activity of regulatory T cells, vitamin D can help to reduce skin inflammation and promote healing.
Overall, these immune mechanisms suggest that vitamin D plays a crucial role in regulating the immune system and reducing skin inflammation by promoting the production of antimicrobial peptides, inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines, and promoting the activity of regulatory T cells.
Is there a link between low Vitamin D levels and Eczema?
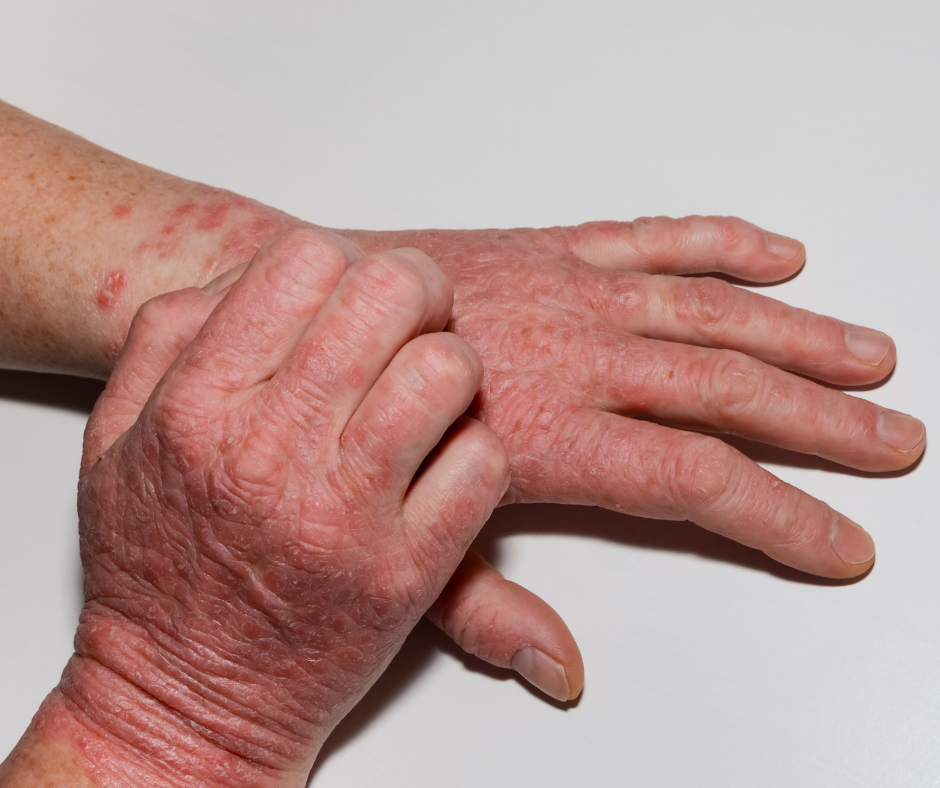
Several studies have shown that individuals with Eczema tend to have lower levels of vitamin D compared to healthy individuals. A study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology found that children with Eczema had lower vitamin D levels than healthy controls and that vitamin D supplementation was associated with significantly improving eczema symptoms.
Another study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology found that topical application of vitamin D3 improved the skin barrier function and reduced inflammation in individuals with Eczema.
In addition to its immunomodulatory effects, vitamin D may also help improve the skin’s barrier function, which is essential for maintaining healthy skin. The skin barrier is made up of lipids, proteins, and other components that help protect the skin from external irritants, such as allergens and pollutants. Vitamin D helps stimulate the production of these components, which can help strengthen the skin barrier and reduce water loss.
While research on the use of vitamin D for Eczema is still ongoing, there is growing evidence that vitamin D may be an effective and safe treatment option for individuals with Eczema. However, it’s important to note that vitamin D supplementation should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as excessive intake of vitamin D can lead to toxicity.
Moreover, vitamin D also plays a role in cell growth and differentiation. It helps regulate the growth and differentiation of various cell types, including skin cells, which can impact skin health and function.
Overall, vitamin D is a vital nutrient that plays a crucial role in many physiological processes in the body, including calcium metabolism, immune function, and cell growth and differentiation.
How can you get your daily dose of Vitamin D?

Vitamin D can be obtained from various food sources, including:
- Fatty fish such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel
- Egg yolks
- Cheese
- Beef liver
- Mushrooms (especially those that have been exposed to UV light)
- Fortified foods such as milk, orange juice, and breakfast cereals.
The most effective way to enhance the production of vitamin D is through exposure to sunlight. When the skin is exposed to sunlight, UVB radiation triggers the production of vitamin D in the skin. It is recommended to expose your skin to direct sunlight for about 10 to 30 minutes, depending on your skin type and the time of day, a few times a week.
Please note that excessive sun exposure can increase the risk of skin cancer, so it’s essential to practice sun safety measures like wearing protective clothing, seeking shade during peak sun hours, and applying sunscreen.
Vitamin D supplements

Obtaining sufficient vitamin D from food alone can be difficult, especially for individuals with limited sun exposure. In such cases, vitamin D supplements may be recommended to meet daily recommended intake levels.
Many vitamin D supplements are available on the market, and choosing a high-quality supplement from a reputable brand is essential. Look for vitamin D3 supplements, as this form is more easily absorbed and utilized by the body than vitamin D2.
The recommended daily vitamin D intake varies depending on age and other factors, so it is best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate dosage for you. Some commonly recommended vitamin D supplements include Nature Made Vitamin D3, Garden of Life Vitamin D3, and Nordic Naturals Vitamin D3.
Generally, adults’ recommended daily vitamin D intake is 600-800 IU (International Units). At the same time, some studies suggest that higher doses benefit individuals with certain health conditions, including Eczema.
It is important to note that while vitamin D supplementation can be helpful for many individuals, it is not a substitute for a balanced and healthy diet or regular sun exposure. Discussing any supplementation with a healthcare professional to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your individual needs is always best.
In conclusion, vitamin D is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in many physiological processes in the body. It helps regulate calcium metabolism, immune function, and cell growth and differentiation. In recent years, studies have shown that vitamin D also significantly impacts skin health and function. It can reduce skin inflammation, promote wound healing, and enhance the skin’s barrier function.
As such, vitamin D supplementation may be a promising treatment option for individuals with Eczema, a skin condition characterized by inflammation and impaired skin barrier function. However, further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms underlying vitamin D’s effects on Eczema and to determine the optimal dosage and duration of vitamin D supplementation for eczema treatment.
By working with your healthcare provider and making other healthy lifestyle changes, you can find relief from eczema symptoms and enjoy healthier, more comfortable skin.
I hope you liked this blog; remember to like, share & subscribe!
Don’t lose hope if you’re dealing with a chronic skin condition.
There is a holistic approach to treatment that can make a real difference in the health of your skin. As a holistic skin specialist, I’ve developed
personalized holistic skin programs that focus on healing your skin from the inside out.
You can take the first step towards achieving natural healing and a brighter future for your skin by scheduling a consultation with me.
Let’s work together to achieve the healthy, glowing skin that you deserve. If you want to learn more about how I can help you, please schedule a consultation.
